X-Ray Cavity Dynamics and Their Role in the Gas Precipitation
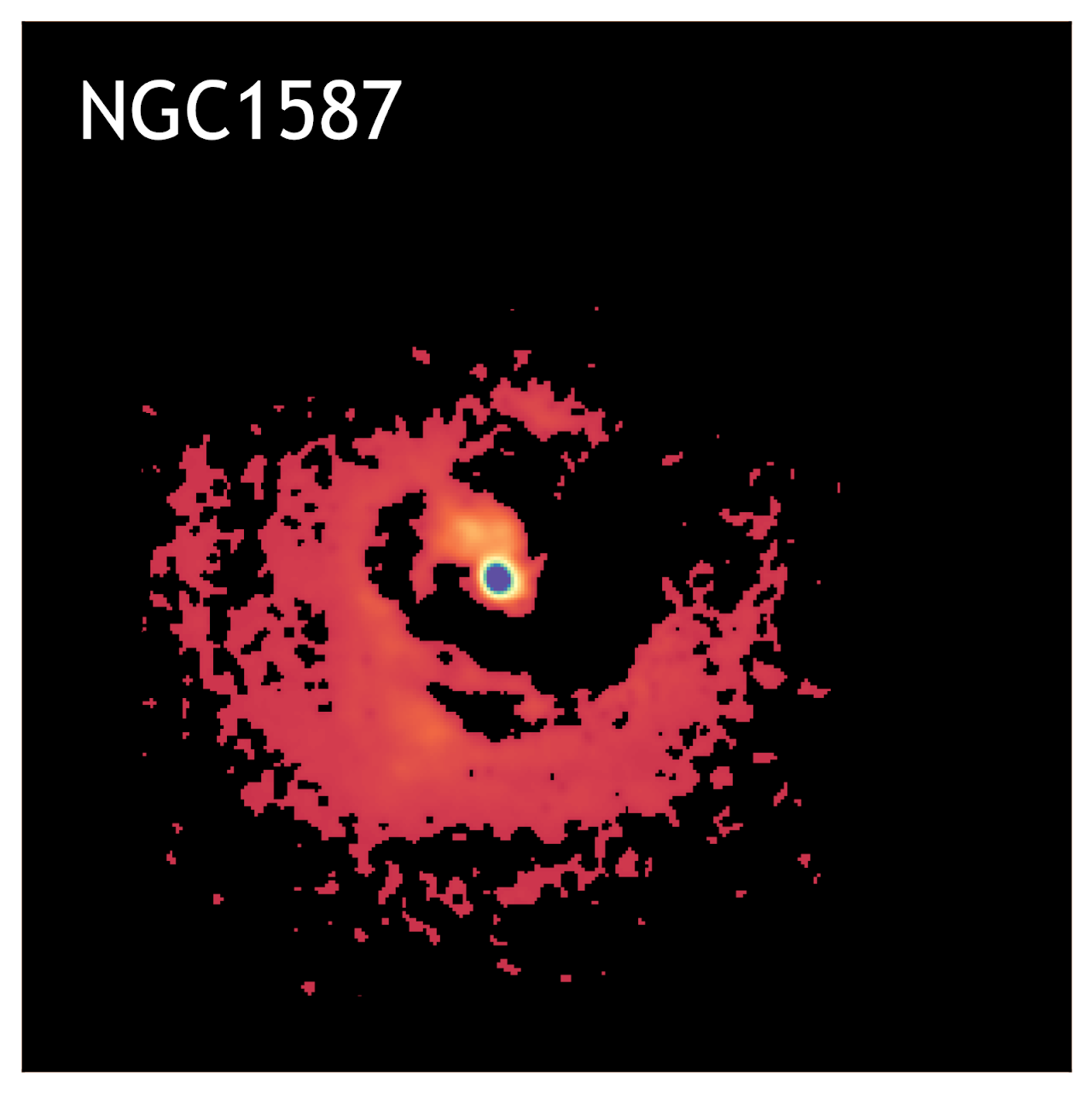
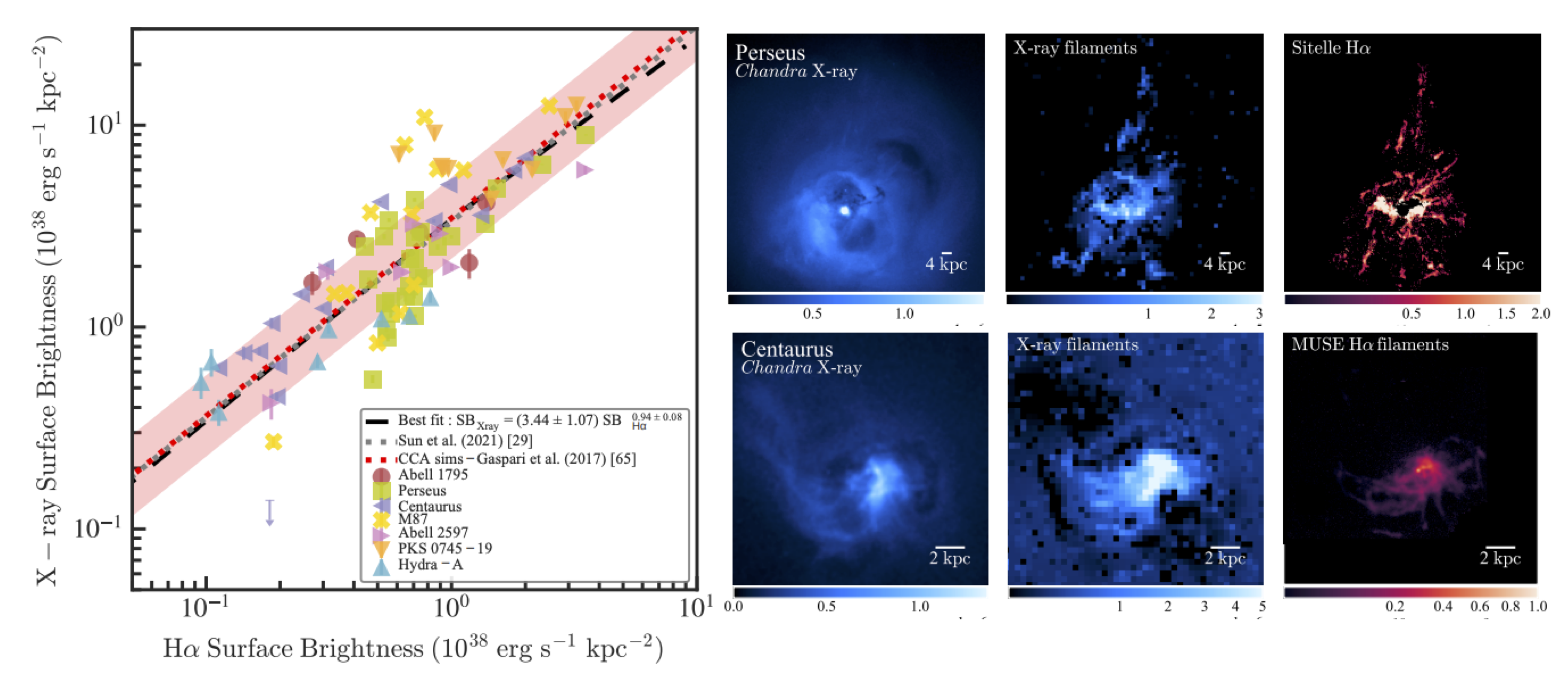
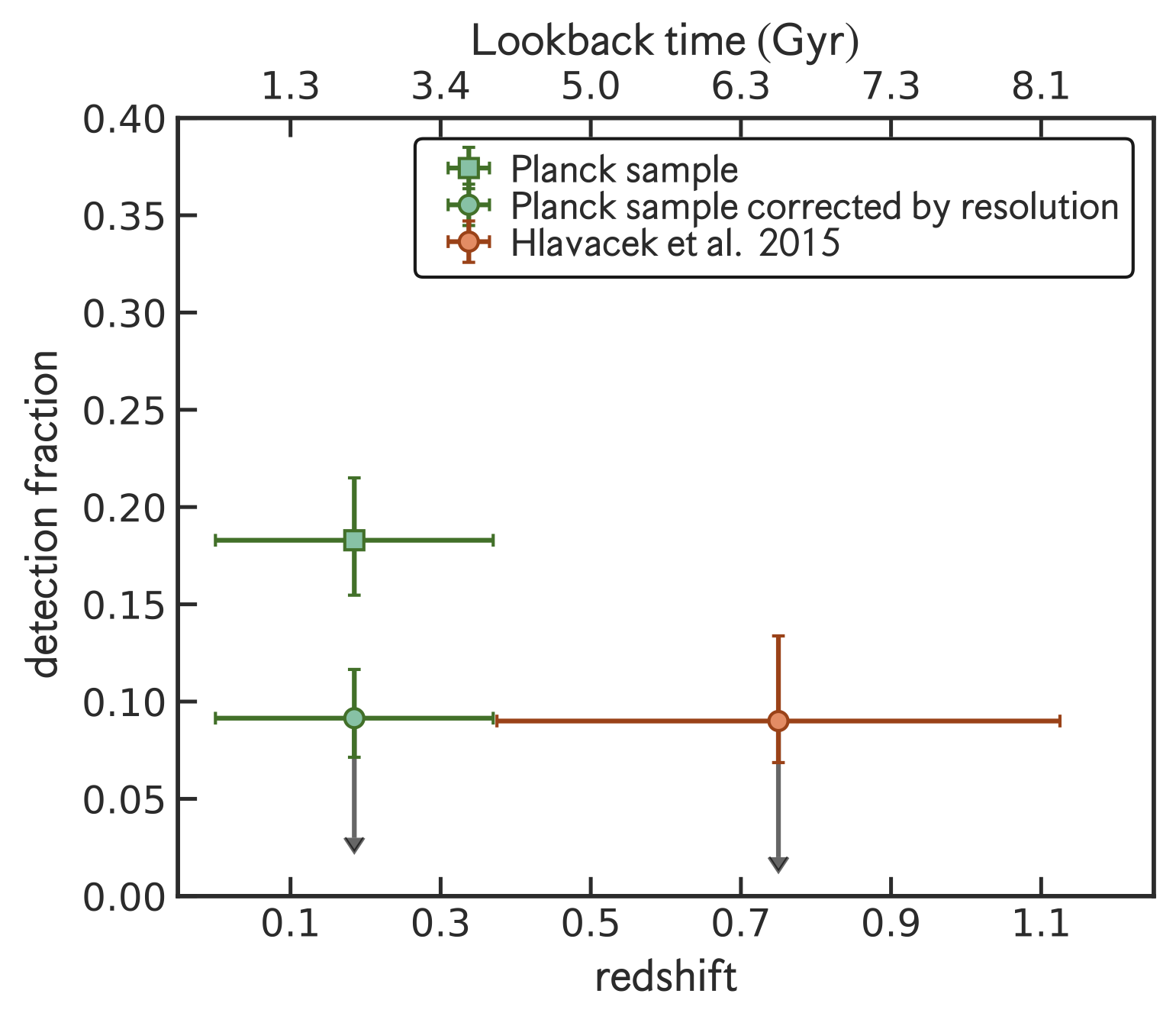
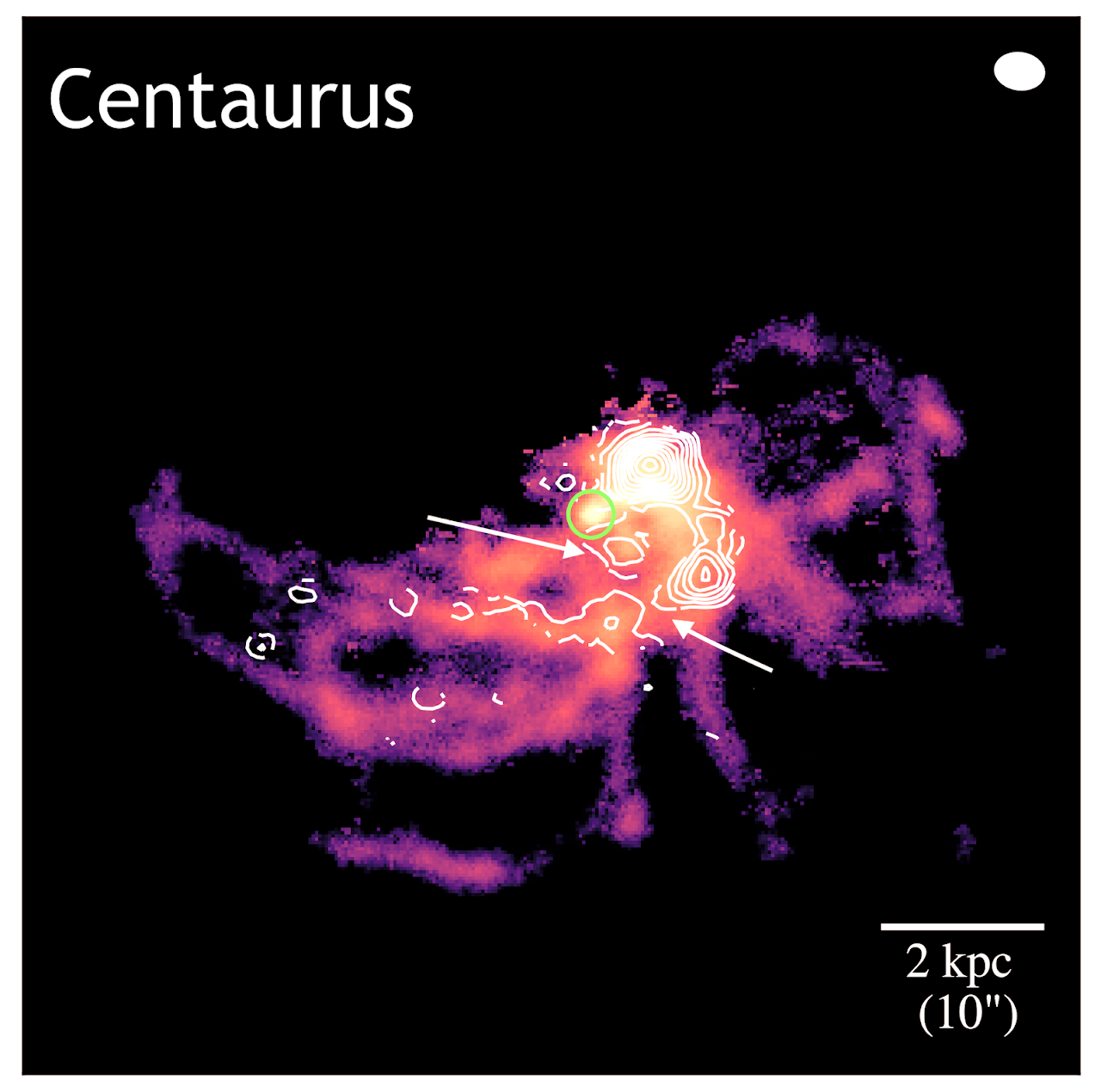
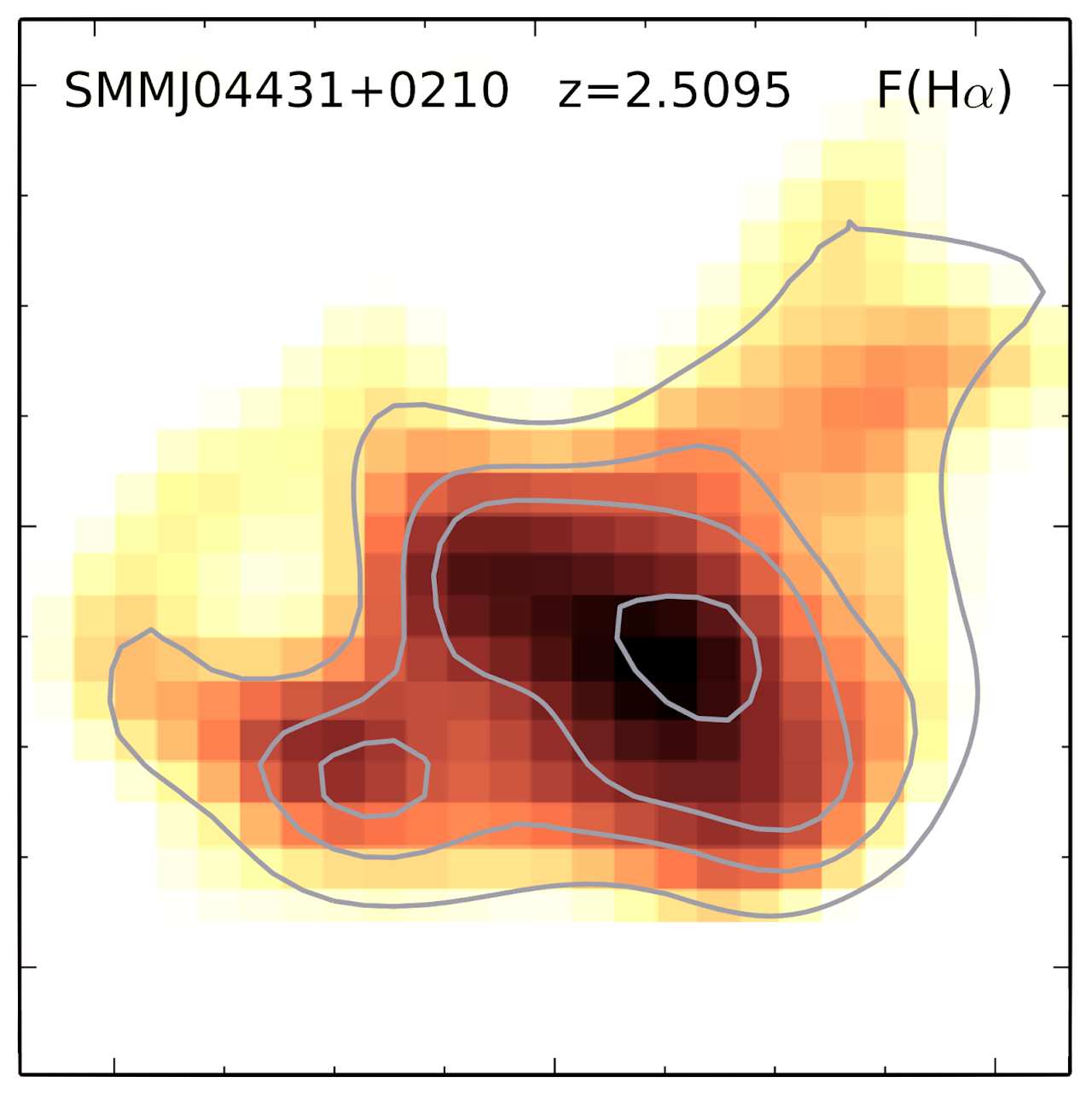
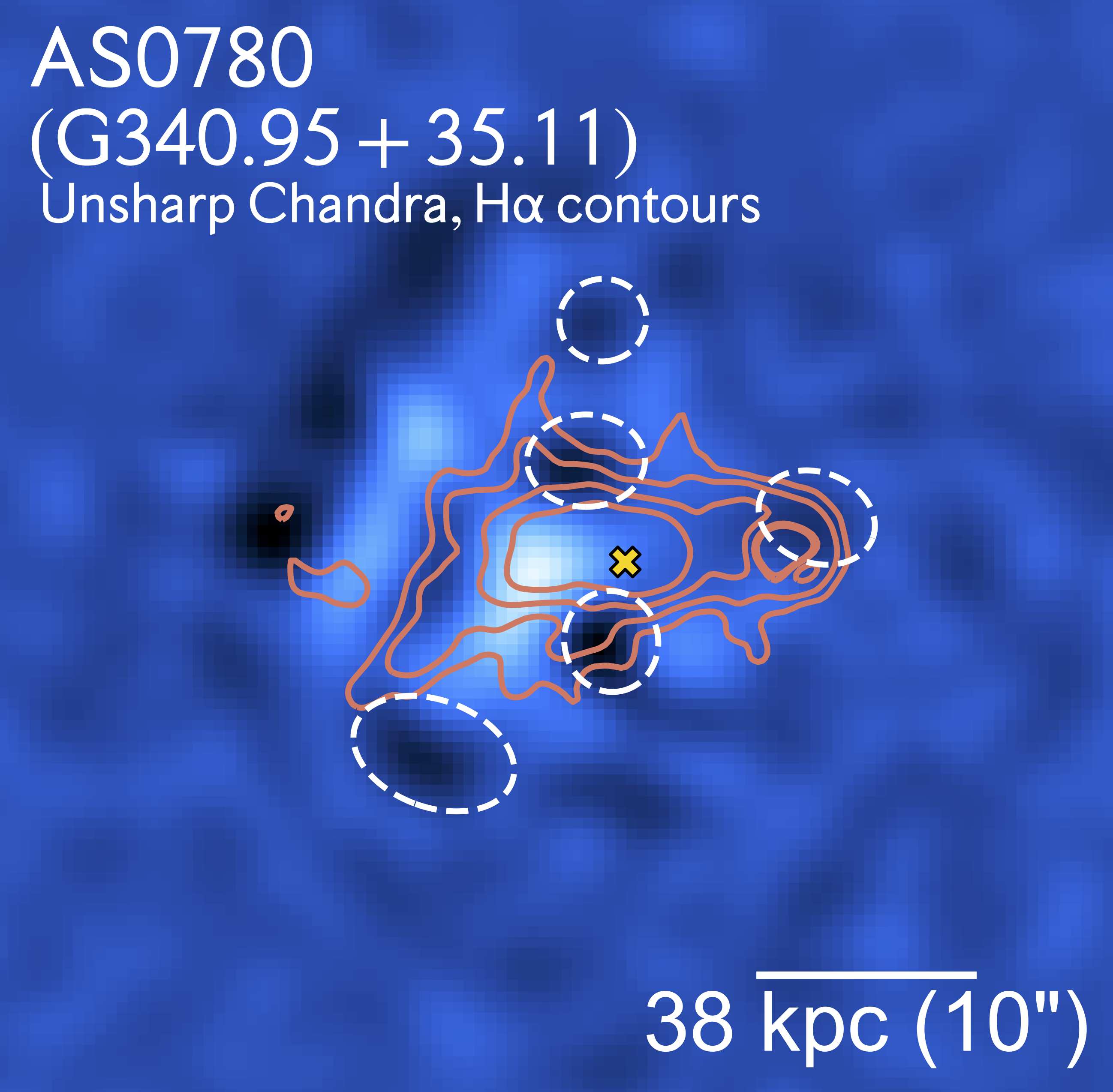
I study the effect of the ICM ``weather'' on the AGN feedback and explore if such is necessary to produce multiphase filaments on a sample of nearby Planck selected galaxy clusters using in synergy Chandra and MUSE observations. We found that most of the multiphase filaments are likely form through AGN feedback, while a few
Learn more
 https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6638-4324
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6638-4324